WHAT IS THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM?
The cannabis plant is incredibly complex, with hundreds of active compounds and a wide array of cultivars to explore. But the real secret to how cannabis interacts with the body lies within all of us, built-in network called the endocannabinoid system, or ECS for short.
Originally discovered in 1988, the ECS plays a central role in how the body processes cannabis. But its purpose goes far beyond weed.
Let’s break down what the endocannabinoid system is, what it does, and how cannabis interacts with it.
What Are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found in cannabis. These are the active ingredients that engage with the ECS. THC and CBD are the most widely known cannabinoids, but there are over 100 others, including CBN, CBG, CBC, and THC-V.
How the Endocannabinoid System Works
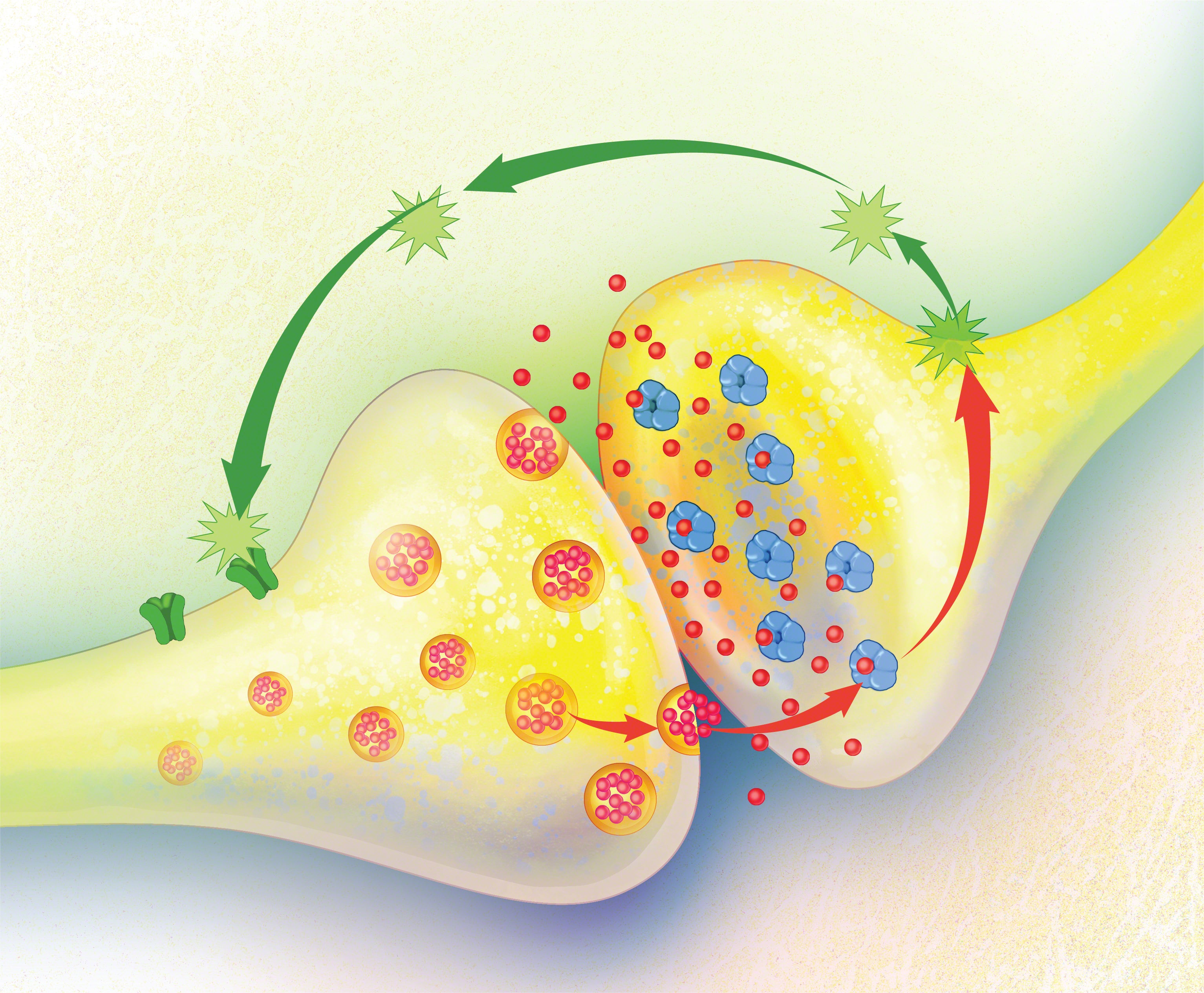
The ECS is part of the larger central nervous system and includes three main parts:
-
Endocannabinoids – the chemical messengers
-
Cannabinoid receptors – located on cell surfaces
-
Enzymes - that break down endocannabinoids after use
There are two primary types of receptors:
-
CB1 receptors, found mostly in the brain and central nervous system
-
CB2 receptors, located mostly in immune tissues and throughout the body

When cannabinoids bind to these receptors, different types of cellular responses are triggered. For example, THC typically engages CB1 receptors, while compounds like beta-caryophyllene are known to bind with CB2 receptors.
The “Bliss Molecule” and Natural Activation
One well-known endocannabinoid is anandamide, nicknamed the “bliss molecule.” It's been associated with positive feelings and may even contribute to what’s often called a “runner’s high.”
Unlike cannabis-derived cannabinoids, anandamide is made on demand and then quickly broken down.
The Entourage Effect
Cannabinoids don’t work in isolation. They interact with other compounds in cannabis, especially terpenes, to produce a synergy known as the entourage effect.
Terpenes are aromatic compounds also found in herbs and spices. Some, like beta-caryophyllene, interact with ECS receptors directly. Others may enhance the absorption or impact of cannabinoids.
Although the entourage effect still needs more clinical study, many consumers and researchers believe that full-spectrum cannabis products that preserve a wide range of cannabinoids and terpenes may better support natural balance than isolated compounds.

How Strains Can Interact Differently with the ECS
Each cannabis strain has a unique chemical fingerprint. This means that even small changes in terpene or cannabinoid content can create different results for each consumer.
For example:
-
Strains rich in beta-caryophyllene may engage CB2 receptors more directly
-
Strains with balanced CBD content may help support the ECS’s internal signaling processes
Because everyone’s ECS is slightly different, finding the right product often takes some personal experimentation.

Is Endocannabinoid Deficiency Real?
Some researchers have proposed a theory called Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency (CECD). This idea suggests that certain conditions may be related to low endocannabinoid levels. While this is still being explored, it’s one of many ways scientists are trying to understand the therapeutic potential of cannabis-derived compounds.
FAQs
To maintain internal balance by regulating key functions.
Yes. The endocannabinoid system is found in nearly all mammals, not just humans.
CB1 is mostly found in the brain and nervous system, while CB2 is located in immune tissues throughout the body.
No. The body produces its own endocannabinoids naturally. Cannabis compounds simply interact with those same receptors.
STIIIZY complies with all applicable state laws regarding the sale and marketing of cannabis products. This content is intended for adults 21+ in jurisdictions where cannabis use is legal under state law. By engaging with this material, you acknowledge that you are of legal age in your jurisdiction.
This content is for informational and educational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or medical condition. STIIIZY makes no health claims about cannabis products. Consult a licensed healthcare professional before using cannabis, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, or have a medical condition.
Cannabis products may affect individuals differently. Consume responsibly and avoid operating vehicles or machinery after use. STIIIZY disclaims all liability for any adverse effects, legal consequences, or misuse resulting from the use of our products or reliance on this content.
Cannabis laws vary by state and locality. This content does not constitute legal advice. Users are responsible for understanding and complying with their local regulations.
Statements about product effects or benefits are based on general industry knowledge and user experiences. Individual results may vary. STIIIZY does not guarantee specific outcomes.
References to third-party studies, testimonials, or external resources are provided for context only. STIIIZY does not endorse or validate these materials unless explicitly stated.
The views and opinions expressed in this blog are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of STIIIZY.

