What Is CBC Cannabinoid? Guide to Cannabichromene in Cannabis
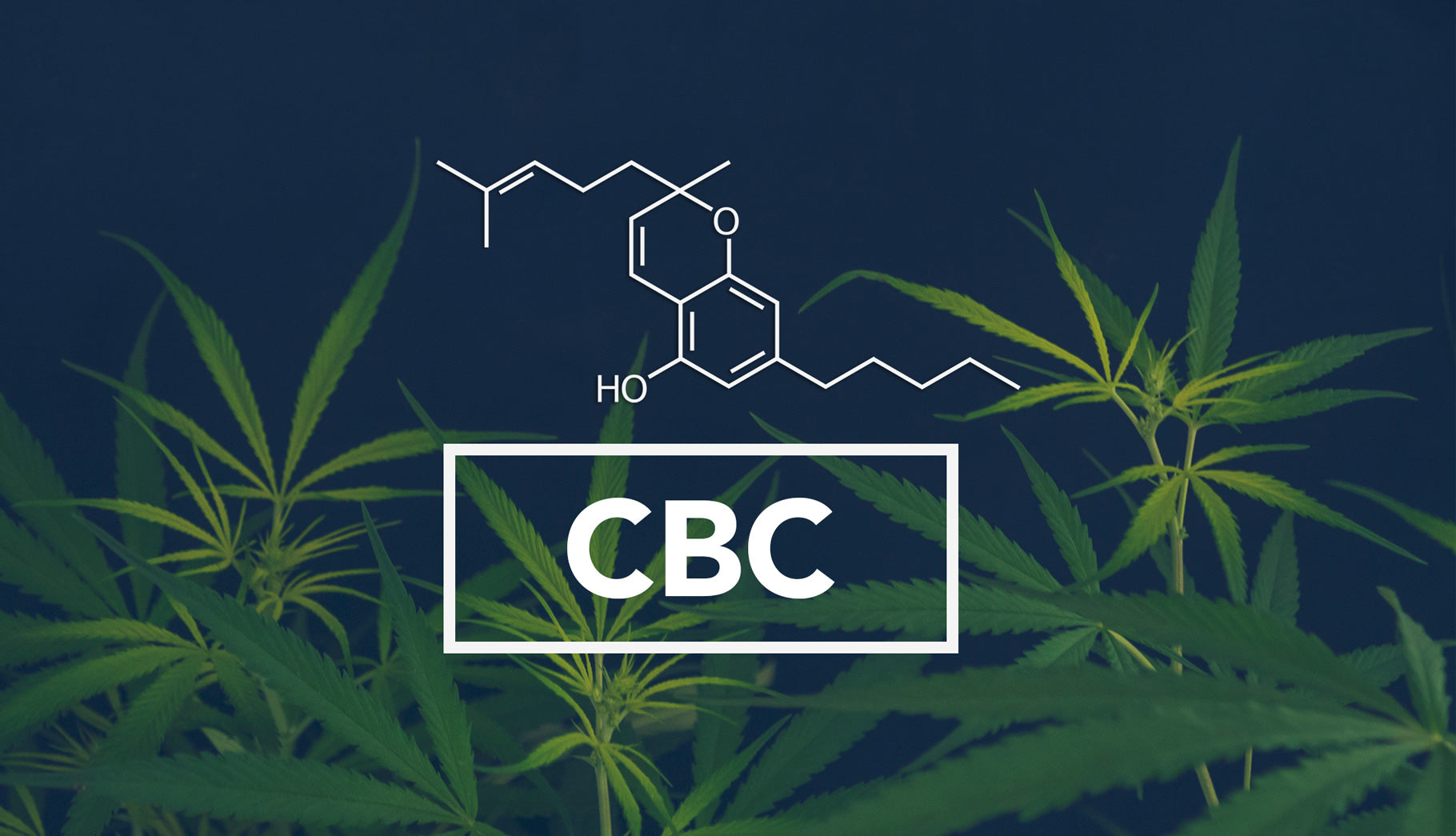
What Is CBC in Cannabis?
Cannabichromene (CBC) is a naturally occurring cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. It’s one of several minor cannabinoids that originate from cannabigerolic acid (CBGa), a common precursor. When CBGa interacts with CBC synthase, it becomes cannabichromenic acid (CBCa). CBCa then converts into CBC through decarboxylation, which is typically triggered by time or heat.
CBC is categorized as non-intoxicating, meaning it doesn't interact with receptors in a way that produces the euphoric effects often associated with other cannabinoids. Instead, it is increasingly recognized as part of the broader chemical spectrum that shapes the overall cannabis experience.
CBC vs. CBD and THC: Key Differences
Although CBC, CBD, and THC all belong to the same cannabinoid family, they behave differently in the body:
| Aspect | CBC | CBD | THC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Psychoactivity | Non-intoxicating | Non-intoxicating | Intoxicating |
| Receptors | TRPV1, TRPA1 | CB1 (indirect), CB2 | CB1 (direct) |
| Interaction | Modulates sensory perception and temperature | Maintains ECS balance | Alters sensory and cognitive perception |
| Product Role | Used in full-spectrum cannabis products | Often in wellness formulations | Central in sensory-forward products |
CBC is particularly known for interacting with vanilloid receptors (TRP channels), making it a valuable contributor in cannabinoid-rich blends.

What Is CBC in Edibles?
CBC is often found in full-spectrum or broad-spectrum edibles. It works alongside other cannabinoids to promote a synergistic experience commonly referred to as the entourage effect.
Common CBC edible formats include:
-
Gummies: Easy to dose and portable.
-
Capsules: Pre-measured for consistent intake.
-
Chocolates: Discreet and flavorful.
-
Baked Goods: Offered in serving-controlled portions.
While CBC doesn’t define the dominant characteristic of an edible, it adds to the overall cannabinoid profile. Edibles typically take longer to activate in the body because they are metabolized through digestion.
Understanding the Entourage Effect
The entourage effect refers to how cannabinoids and terpenes interact to create a layered cannabis experience. CBC, while subtle in its solo behavior, plays a role in enhancing this effect by interacting with THC, CBD, CBG, and other compounds.
This interplay helps cannabis formulations feel more complete compared to isolates. The combined presence of cannabinoids may influence how the body processes and integrates each compound. CBC's presence in full-spectrum blends is one way this effect can be explored.

Common CBC Product Types
CBC can be found in several product formats that cater to various lifestyles and preferences.
1. CBC Oils and Tinctures
Oils containing CBC often include a full cannabinoid profile. These are typically taken sublingually (under the tongue) or mixed into foods. They are valued for customizable intake and precise control.
2. CBC Edibles
Edibles infused with CBC offer long-lasting effects and discreet use. They are ideal for individuals looking for steady cannabinoid presence throughout the day.
3. CBC Topicals
Used externally, CBC topicals combine cannabinoids for localized application. These products are typically crafted as balms, salves, or roll-ons and are designed for direct contact without systemic effects.
4. CBC Capsules
Encapsulated CBC provides a consistent cannabinoid profile. These are often favored for ease of use and predictability in intake.
Insights on CBC in Cannabis Formulations
While CBC is less well-known than major cannabinoids like THC and CBD, it holds growing relevance in cannabis science. Researchers are studying CBC's influence on sensory pathways and its compatibility with other plant compounds.
Within consumer formulations, CBC's value lies in its versatility and ability to blend seamlessly into balanced cannabinoid products. Brands use it to diversify cannabinoid ratios, refine product profiles, and broaden appeal among those seeking more nuanced experiences.
FAQs About CBC
Is CBC intoxicating?
No, CBC is considered non-intoxicating and does not produce euphoric effects.
How is CBC different from CBD?
CBC interacts primarily with TRP receptors, while CBD influences CB1 and CB2 receptors indirectly.
Can CBC be used in edibles and topicals?
Yes. CBC can be infused into edibles, oils, tinctures, and topicals.
Does CBC appear in full-spectrum products?
Yes. CBC is a common component of full-spectrum formulations, especially those highlighting minor cannabinoids.
Where can I find CBC products?
Look for licensed dispensaries that offer full-spectrum oils, tinctures, or infused edibles featuring minor cannabinoids.
FAQs
CBC interacts primarily with TRP receptors, while CBD influences CB1 and CB2 receptors indirectly.
STIIIZY complies with all applicable state laws regarding the sale and marketing of cannabis products. This content is intended for adults 21+ in jurisdictions where cannabis use is legal under state law. By engaging with this material, you acknowledge that you are of legal age in your jurisdiction.
This content is for informational and educational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or medical condition. STIIIZY makes no health claims about cannabis products. Consult a licensed healthcare professional before using cannabis, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, or have a medical condition.
Cannabis products may affect individuals differently. Consume responsibly and avoid operating vehicles or machinery after use. STIIIZY disclaims all liability for any adverse effects, legal consequences, or misuse resulting from the use of our products or reliance on this content.
Cannabis laws vary by state and locality. This content does not constitute legal advice. Users are responsible for understanding and complying with their local regulations.
Statements about product effects or benefits are based on general industry knowledge and user experiences. Individual results may vary. STIIIZY does not guarantee specific outcomes.
References to third-party studies, testimonials, or external resources are provided for context only. STIIIZY does not endorse or validate these materials unless explicitly stated.
The views and opinions expressed in this blog are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of STIIIZY.

